Introduction
In an ever-evolving digital landscape, businesses are continuously seeking innovative strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
One of the newest waves sweeping across the commerce sector is Composable Commerce.
It offers businesses the agility and flexibility they need to meet the changing demands of consumers.
But what exactly is Composable Commerce? How does it relate to Microservices, PBCs, and MACH architecture?
And why is it becoming the preferred choice for B2B businesses?
Let’s delve into these questions and more.
What is Composable Commerce?
Composable Commerce is an approach to ecommerce that gives businesses the flexibility to build a customised commerce platform by selecting and integrating various commerce services according to their unique business requirements.
Unlike traditional monolithic platforms, Composable Commerce allows businesses to leverage the best-of-breed services that align with their particular needs.
Services such as inventory management, payment processing, customer relationship management (CRM), order management, content management, and more can be composed together into a bespoke ecommerce platform that fits the business’s needs perfectly.

The core philosophy behind Composable Commerce is flexibility and modularity.
It is a particularly relevant concept in today’s digital age where customer expectations and market dynamics are in constant flux.
When you plan your web design strategy meeting, it is essential to give some importance to this topic and analyse the need for composable commerce in detail.
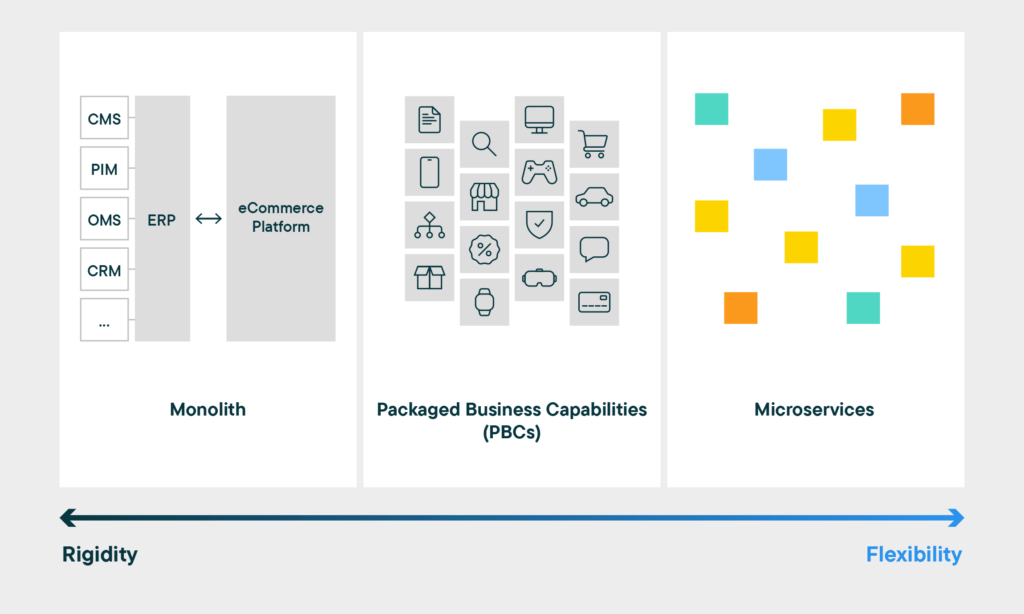
Microservices vs. Package Based Components (PBCs)
To understand Composable Commerce, it’s crucial to grasp the distinction between Microservices and Package Based Components (PBCs).
Microservices are small, independent services that each perform a specific function.
They can be independently developed, deployed, and scaled, which makes them ideal for composing a flexible ecommerce platform.
On the other hand, Package Based Components (PBCs) are pre-packaged software modules that can be reused across different systems. These components offer more structure and standardization compared to microservices, but they might not provide the same level of flexibility and independence.
While both Microservices and PBCs have their pros and cons, the choice between them often depends on the specific needs and capabilities of the business.
Microservices can offer more flexibility and scalability, but they can also be more complex to manage. PBCs, meanwhile, can simplify development and maintenance, but they might not offer the same level of customisation.
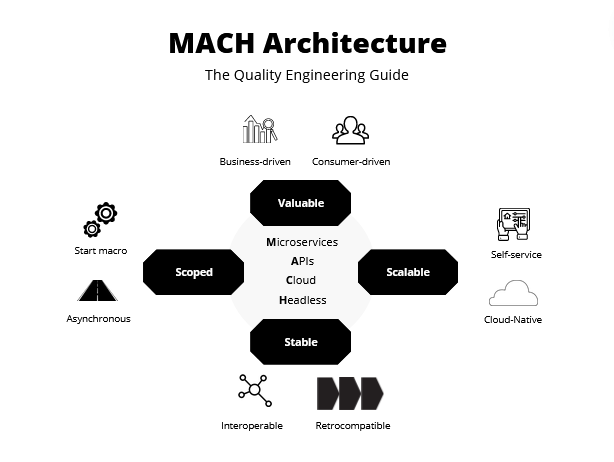
The Role of MACH Architecture
The rise of Composable Commerce is intrinsically linked to the MACH (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, Headless) architecture.
This technology architecture is built to support the principles of Composable Commerce.
Microservices form the basis of the architecture, allowing each function to be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) facilitate the interaction and data exchange between these services, ensuring a seamless integration of functions.
Cloud-native design ensures scalability and flexibility while reducing the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure.
And finally, headless architecture separates the frontend and backend, enabling businesses to innovate and customise their customer-facing experience without disrupting backend operations.
Why B2B Businesses Choose Composable Commerce
Composable Commerce is increasingly becoming the choice for B2B businesses due to its flexibility and scalability. It allows businesses to quickly adapt to changing market dynamics and customer needs.
Instead of being locked into a one-size-fits-all solution, B2B businesses can customise their commerce platform to their unique needs, leading to more efficient operations and better customer experiences.
Moreover, as B2B commerce becomes more complex and sophisticated, businesses require a platform that can support advanced functionalities like personalised pricing, custom catalogs, and complex order management.
Composable Commerce, with its modular approach, allows businesses to easily incorporate these features.
Developing Your Composable Enterprise
When developing aComposable Enterprise, businesses should consider a few critical factors:
- Business Requirements: Understand your unique business needs and choose the services that align with these requirements. This could include specific features, scalability needs, or integration requirements with existing systems.
- Flexibility and Modularity: Opt for services that offer the flexibility to be modified or replaced as your business needs evolve. The services should also be modular, allowing you to add or remove components as needed.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the services can be seamlessly integrated together. This requires robust APIs that can facilitate data exchange and interaction between services.
- Technical Support: Consider the level of technical support provided by the service vendors. This is especially important if your business does not have extensive in-house technical resources.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that the services meet the necessary security and compliance standards. This is particularly crucial for businesses in regulated industries.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the services, including the upfront implementation cost and the ongoing maintenance cost. Opt for a solution that offers a good balance between cost and functionality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Composable Commerce is a transformative approach to eCommerce that offers businesses unparalleled flexibility and adaptability. By leveraging Microservices, PBCs, and MACH architecture, businesses can build a custom eCommerce platform that perfectly suits their needs.
This approach is particularly beneficial for B2B businesses, which require advanced functionalities and a high degree of customization.
An essential aspect of this customisation is eCommerce website design. Composable Commerce allows businesses to design their eCommerce website in a way that reflects their brand and meets their specific needs, from the user interface to the underlying functionalities.
However, building a Composable Enterprise requires careful consideration of various factors, including business requirements, flexibility, integration capabilities, technical support, security, and cost. eCommerce website design is a critical component of this, as the design can significantly influence the customer experience and overall success of the commerce platform.
With the right approach and support, Composable Commerce can enable businesses to create an eCommerce website design that not only looks great but also offers a seamless and efficient user experience. This ultimately leads to increased customer satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and improved business performance.
So, as we move forward in this digital age, Composable Commerce and eCommerce website design will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of B2B commerce.